Analysis of an HIV - HCV simultaneous infection model with time delay
Keywords:
Delay, IV/HCV simultaneous infection, reproduction number, equilibrium, stabilityAbstract
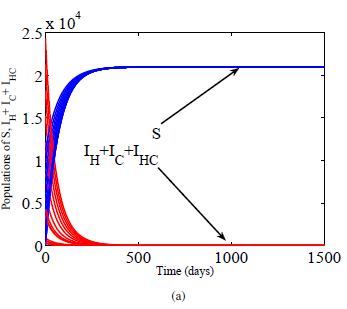
A novel mathematical delay model for simultaneous infection of HIV and hepatitis C virus is formulated and dynamically analyzed. Basic properties of the model are established and proved. Basic reproductive threshold is systematically calculated as the maximum of three subthreshold parameters. A disease free equilibrium is determined to be globally asymptotically stable for all values of the delay when the threshold is less than unity. However, when the threshold is greater than one, endemic equilibrium emerged which is shown to be locally asymptotically stable for any length of delay. Although the delay has no effect on stabilities of equilibria points, however, it is found to reduce the infectivity of the viruses as the length of the delay is increased. Epidemiological interpretations of the results and numerical simulations illustrating them are given.