Virtual Screening of Selected Natural Products as Human Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1 Blockers
Keywords:
Human tyrosinase-related protein 1, skin lightening, Hydroquinone, Tropolone, SalicinAbstract
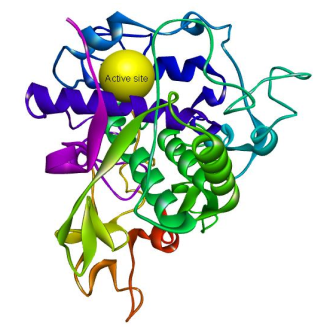
Many researchers have widely explored the need to replace the harmful compound hydroquinone in skin-lightening creams with more skin-friendly compounds that can give similar results. Some compounds from the plant kingdom have been shown to possess human tyrosinase inhibitory action with no adverse effect on the skin. In this study, the virtual screen of glabridin, kojic acid, arbutin, niacinamide, ascorbic acid, salicin, lactic acid, glutathione, azelaic acid, linoleic acid, glycolic acid, acclaimed to possess this activity as well as the synthetic compound hydroquinone, as human tyrosinase-related protein 1 inhibitor was investigated using computational methods. Site-directed docking was performed at the binding pocket on the enzyme carrying the cocrystallized ligand tropolone. The binding affinity of salicin (-6.7 kcal/mol), a-arbutin (-6.3 kcal/mol), glutathione (-6.2 kcal/mol), ascorbic acid (-5.7 kcal/mol), and niacinamide (-5.7 kcal/mol) were higher than that of the cocrystallized ligand tropolone (-5.5 kcal/mol) and the synthetic skin lightening compound hydroquinone (-4.8 kcal/mol). a-arbutin and glutathione also interacted with similar amino acids units as hydroquinone, suggesting that they followed the exact mechanism of action. These findings strongly corroborate the claim that these natural products could inhibit melanin production and may serve to replace hydroquinone in skin lightening creams.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




