Statistical Analysis and Distribution of Global Solar Radiation and Temperature Over Southern Nigeria
Keywords:
Global solar radiation, temperature, Box plots, Mann-Kendall test, Gaussian distribution, linear regression, Sen's slope estimateAbstract
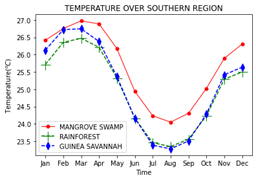
The intensity of solar energy that is received by a particular location is affected by most meteorological conditions including, the solar irradiance received by the location, precipitation, extreme heat as a result of the surface or ambient temperature, etc. We obtain the monthly global solar irradiation and ambient temperature for the three (3) eco-climatic zones in the south of Nigeria (17 locations) for 12 years (2005 - 2016) from the Photovoltaic Geographical Information System (PVGIS) Satellite. The goal of this study is to understand how regional meteorological conditions affect radiation and temperature reception. Monthly and annual trends were plotted and compared for both variables in each region to show the similarity or dichotomy in their trends. The Mann-Kendall (M-K) trend test has been adopted to reveal that the changes in the variations on an annual basis, and results showed that the trend were not significant for both variables. Box plots have been used to give a better description of the data, and compared to show similarities and differences. Finally, we adopted the Gaussian (normal) distribution to show, understand and compare the data distribution. Linear regression plots for each zone shows that the relationship between the solar irradiation and temperature is high. Results show that the climate and vegetation of a region contributes majorly to the variation of radiation and temperature. Inhomogeneity
of data or results for locations in the same zones may be attributed to local meteorological conditions. The results obtained here will prove vital in decision making relating to the adoption of solar energy technologies in the region. Results show that the climate and vegetation of a region contributes majorly to the variation of radiation and temperature. Inhomogeneity of data or results for locations in the same zones may be attributed to local meteorological conditions.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 M. A. Okono, E. P. Agbo, B. J. Ekah, U. J. Ekah, E. B. Ettah, C. O. Edet

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





