Optimization by Box Behnken Design for Eosin Yellow Dye Removal from Aqueous Medium using Date Palm Seeds-Porous Carbon@TiO2 Blend
Keywords:
Porous carbon, TiO2, Adsorption, Eosin yellow dye, Box Behnken designAbstract
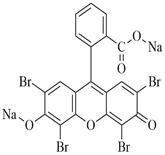
Biological stains are potentially harmful compounds present in the environment, in which Eosin yellow dye (EYD) is one of the most commonly applied stains. In this research, date palm seeds-porous carbon (DPSC) and its TiO2 blend (TiO2-DPSC) were prepared and their efficiency on the removal of EYD from an aqueous medium was investigated. Characterization by SEM, EDX, FTIR and BET surface area was performed on the materials. The BET surface area (542.63 m2/g) and pore diameter (2.02 nm) of TiO2-DPSC were found to be higher than that of DPSC (332.74 m2/g and 1.85 nm) indicating that TiO2-DPSC is mesoporous while DPSC is microporous. The major and interactive impacts of the adsorption parameters: initial EYD concentration, pH, adsorbent dose, and time of contact were examined by Box Behnken design in response surface methodology. The high R2 values 0.9658 and 0.9597 for DPSC and TiO2-DPSC agreed with the adjusted R2 values suggesting the quadratic model sufficiently interprets the adsorption data. The optimum removal efficiency of EYD onto DPSC and TiO2-DPSC was 34.63 mg/g and 55.34 mg/g which are in agreement with the predicted removal of 34.75 mg/g and 50.11 mg/g respectively at the center point values of Co=300 mg/L, pH 2, 362.5 min and 0.1 g adsorbent dose. The results also showed the acceptability of the Box Behnken design in response surface methodology for the optimization of EYD removal from aqueous media using DPSC and TiO2-DPSC blends. Hence, better EYD removal reported in TiO2-DPSC compared to DPSC was due to its improved adsorptive features.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





